L-glycine or glycine is one of the 22 amino acids that is essential for your body to be able to function properly and for you to be able to produce the necessary proteins. In fact, L-glysine is the smallest of the amino acid, as well as, the simplest. Just because it is the smallest amino acid doesn’t mean it doesn’t play an important role in a number of biochemical reactions. In your body’s enzymes and proteins, there is only one other amino acid that is more wide spread than L-glycine. 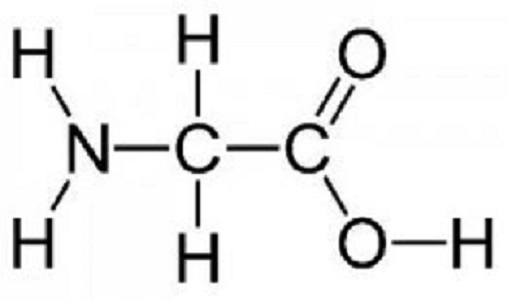
Your body is able to produce glycine because it is a non-essential amino acid. It can also be taken in supplement form. You can get glycine from fish, poultry, dairy and meat. You can take a glycine supplement. If you take an HGH supplement like GenF20 Plus you’ll find L-glycine as one of the main ingredients, because not only can it help increase HGH production, which has tons of benefits, L-glycine supports many of those benefits on its own. Glycine is biosynthesized in the liver from the amino acids serine and threonine.
The Role of Glycine
Glycine is an important amino acid and it plays an important role in many functions within the body, which we will look at in more detail. L-glycine is needed to produce nucleic acids, bile acids, creatine phosphates and porphyrins. It regulates and supports many processes that are necessary for body function.
Glycine plays an important role in the development of healthy RNA and DNA, necessary for proper cell function. Glycine is one of the three amino acids that forms creatine. It also promotes muscle growth and increases workout energy, so you can see how it can be beneficial in the HGH supplement GenF20 Plus.
#1 Your Metabolism
Glycine, is a glucogenic amino acid that regulated the release of blood sugars within your liver and fat stores to help your metabolism function optimally. It provides glucose to your body for energy and it boosts your metabolism. Glycine can be beneficial to those who are suffering from chronic fatigue, hypoglycemia, or anemia.
#2 Your Nervous System
Glycine affects your nervous system. Glycine affects your brain’s neurotransmitters, which are needed to balance emotions and maintain brain function. The central nervous system uses equally glycine, taurine and GABA as inhibitory neurotransmitter functioning in the brain stem and spinal cord where nerve impulses are transmitted. Glycine removes potassium and chloride so that is can regulate nervous system neurons for hyper excitability.
#3 Your Mental Health
Numerous studies have looked at how amino acids can help hyperactivity, treat bipolar, schizophrenia and epilepsy. One study that looked at schizophrenic patients where treatments weren’t effective found that when high doses of glycine were administered in conjunction with anti-psychotic medications the negative symptoms associated with schizophrenia and mental illness in general were eliminated. Numerous other psychological disorder studies confirmed these findings,1,2 while other studies found that epileptic seizures were eliminated with glycine.3,4
Glycine was also found to help with sleep disorders and cases of insomnia. In 2007 the journal “Sleep and Biological Rhythms printed the results of investigators who found a glycine supplement significantly improved sleep quality.
#4 Your Digestive Health
Glycine plays a key role in the function of the digestive system. Your gallbladder contains high glycine levels, which help in the production of bile required to digest those dietary fats.
A study in 2006 that was published in the “Journal of Pharmaceutical Science” found that glycine balances the digestive tract acid ratio, which is why glycine is found in antacid products.
#5 Cancer Treatments
Earlier studies have shown that glycine could play a role in the treatment of some cancers. It was also found to prevent the formation of melanoma and to prevent cancerous tumors forming. Another study found that glycine subdued angiogenesis and stopped the growth of tumors.5
#6 Your Muscle Growth
Glycine is necessary for creatine biosynthesis to occur. This is your muscles direct energy source that helps in the building of muscle tissue and muscle strength. Athletes looking to increase their lean muscle mass will use a glycine supplement. When mobility is an issue glycine can also be helpful.
#7 Regulate Your Blood Sugar Levels
Glycine helps to regulate your blood sugar levels. It converts glucose to usable energy. Research has shown that glycine improves blood sugar in type 2 diabetes sufferers and it can do this long-term.6,7 Because glycine is sweet, it is sometimes recommended as a sugar substitute for those with diabetes
#8 Anti Aging
Glycine is an important amino acid in slowing the aging process. 33% of your collagen is made of glycine. Collagen is a necessary protein to keep your skin smooth, firm and pliable. When there isn’t enough glycine, your skin cells and tissue can’t repair itself.
#9 Free Radicals
There has also been a great deal of research that shows glycine protects your body from shock in the event of blood loss and it helps to stop the formation of free radicals.8
#10 Regulate Hormones
Glycine is methylated into DMG, which plays a major role in the carbon pathway needed for the biosynthesis of steroids. It also stimulates HGH production and secretion.
Conclusion
Glycine is not associated with any serious side effects. Occasionally stomach upset, nausea, drowsiness or vomiting may occur. Glycine is very important in the body, especially when it comes to the digestive and central nervous system maintenance. It is one of the common amino acids found in human proteins.
The HGH supplement GenF20 Plus contains 100 mg of Glycine. We’ve looked in detail at the benefits of glycine. GenF20 Plus helps to reduce the signs of aging, increase lean muscle mass, decrease fat and much more. Glycine is a powerful ingredient that plays a key role in the GenF20 Plus and it also helps to increase HGH production.
Resources:
1 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9272487
2 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8932891
3 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17041593
4 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9708551
5 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10334195
6 http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/34/1/162.full
7 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2696340
8 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11939124











